Maximizing Trauma Surgery Outcomes: Best Practices
- danlimsf
- Aug 20, 2025
- 4 min read
Trauma surgery is a critical field that requires precision, skill, and a deep understanding of human anatomy. Every decision made in the operating room can significantly impact a patient's recovery and overall outcome. In this blog post, we will explore best practices that can help maximize trauma surgery outcomes.
By focusing on preparation, teamwork, and post-operative care, we can improve the chances of a successful recovery for trauma patients.
Understanding Trauma Surgery
Trauma surgery involves the treatment of injuries caused by accidents, falls, or violence. These injuries can range from minor wounds to life-threatening conditions.
Surgeons must act quickly and efficiently to stabilize patients and perform necessary procedures.
The complexity of trauma cases often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving various specialists.
Preoperative Preparation
Effective trauma surgery begins long before the patient enters the operating room.
1. Comprehensive Assessment
A thorough assessment of the patient's condition is crucial.
History Taking: Gather information about the incident, medical history, and any medications the patient is taking.
Physical Examination: Conduct a detailed physical exam to identify all injuries.
Imaging Studies: Utilize X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to get a clear picture of the injuries.
This comprehensive assessment helps in formulating a tailored surgical plan.
2. Team Coordination
Trauma surgery is a team effort.
Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles of each team member, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses.
Preoperative Briefing: Hold a briefing to discuss the surgical plan, potential challenges, and individual responsibilities.
Effective communication and coordination can prevent errors and improve outcomes.
Surgical Techniques
The techniques used during surgery can greatly influence recovery.
1. Minimally Invasive Approaches
Whenever possible, opt for minimally invasive techniques.
Benefits: These methods often result in less pain, shorter recovery times, and reduced risk of infection.
Examples: Laparoscopic surgery is a common minimally invasive technique used in trauma cases.
By minimizing tissue damage, patients can recover more quickly.
2. Precision and Care
During surgery, precision is key.
Attention to Detail: Surgeons should focus on meticulous techniques to minimize complications.
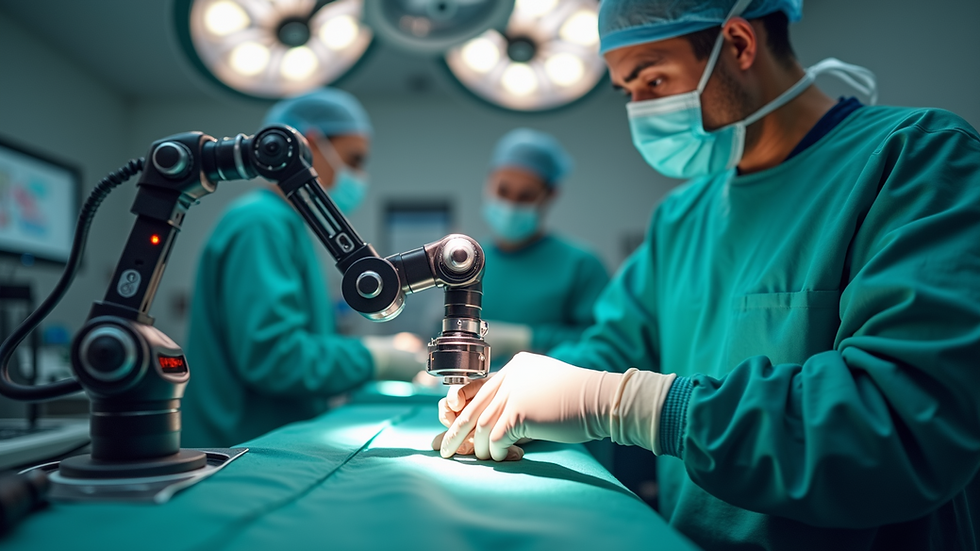
Use of Technology: Incorporate advanced technologies, such as robotic-assisted surgery, to enhance precision.
The more precise the surgery, the better the outcomes.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care is just as important as the surgery itself.
1. Monitoring and Support
After surgery, continuous monitoring is essential.
Vital Signs: Regularly check vital signs to detect any complications early.
Pain Management: Implement effective pain management strategies to enhance comfort and recovery.
Proper monitoring can help identify issues before they become serious.
2. Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in recovery.
Physical Therapy: Initiate physical therapy as soon as possible to regain strength and mobility.
Patient Education: Educate patients about their recovery process and what to expect.
A well-structured rehabilitation program can significantly improve outcomes.
The Role of Technology
Technology is transforming trauma surgery.
1. Advanced Imaging
Utilizing advanced imaging techniques can enhance surgical planning.
3D Imaging: This technology allows surgeons to visualize complex injuries in detail.
Real-Time Imaging: Intraoperative imaging can guide surgeons during procedures.
By leveraging technology, surgeons can make more informed decisions.
2. Data Analytics
Data analytics can improve surgical outcomes.
Outcome Tracking: Collect and analyze data on surgical outcomes to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Predictive Analytics: Use predictive models to assess risks and tailor treatment plans.
Data-driven decisions can lead to better patient care.
Building a Culture of Safety
Creating a culture of safety is essential in trauma surgery.
1. Team Training
Regular training sessions can enhance team performance.
Simulation Drills: Conduct simulation drills to practice emergency scenarios.
Feedback Mechanisms: Implement systems for providing feedback on performance.
A well-trained team is better equipped to handle the challenges of trauma surgery.
2. Open Communication
Encourage open communication among team members.
Reporting Systems: Establish systems for reporting errors or near misses without fear of punishment.
Regular Meetings: Hold regular meetings to discuss cases and share insights.
Open communication fosters a safer environment for patients.
Engaging with Patients
Patient engagement is crucial for successful outcomes.
1. Informed Consent
Ensure that patients understand their treatment options.
Clear Explanations: Provide clear explanations of procedures, risks, and benefits.
Encourage Questions: Allow patients to ask questions and express concerns.
Informed patients are more likely to be satisfied with their care.
2. Emotional Support
Trauma can have emotional impacts on patients.
Counseling Services: Offer access to counseling services for emotional support.
Support Groups: Encourage participation in support groups for trauma survivors.
Addressing emotional needs can enhance overall recovery.
Continuous Improvement
The field of trauma surgery is always evolving.
1. Research and Innovation
Stay updated on the latest research and innovations.
Clinical Trials: Participate in clinical trials to explore new techniques and treatments.
Professional Development: Attend conferences and workshops to learn from experts.
Continuous learning can lead to improved practices and outcomes.
2. Quality Improvement Initiatives
Implement quality improvement initiatives within your practice.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of surgical outcomes to identify areas for improvement.
Benchmarking: Compare outcomes with other institutions to set performance goals.
Quality improvement efforts can lead to better patient care.
The Future of Trauma Surgery
As we look to the future, several trends are emerging in trauma surgery.
1. Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is becoming more prevalent.
Tailored Treatments: Use genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients.
Precision Surgery: Focus on precision techniques that cater to the unique needs of each patient.
Personalized approaches can enhance surgical outcomes.
2. Telemedicine
Telemedicine is changing how we provide care.
Remote Consultations: Use telemedicine for preoperative and postoperative consultations.
Follow-Up Care: Implement telehealth solutions for follow-up care and monitoring.
Telemedicine can improve access to care and enhance patient engagement.
Final Thoughts
Maximizing trauma surgery outcomes requires a multifaceted approach.
From thorough preoperative assessments to effective postoperative care, every step matters.
By focusing on teamwork, technology, and patient engagement, we can improve the chances of successful recovery for trauma patients.
As the field continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to achieving the best possible outcomes.
Comments